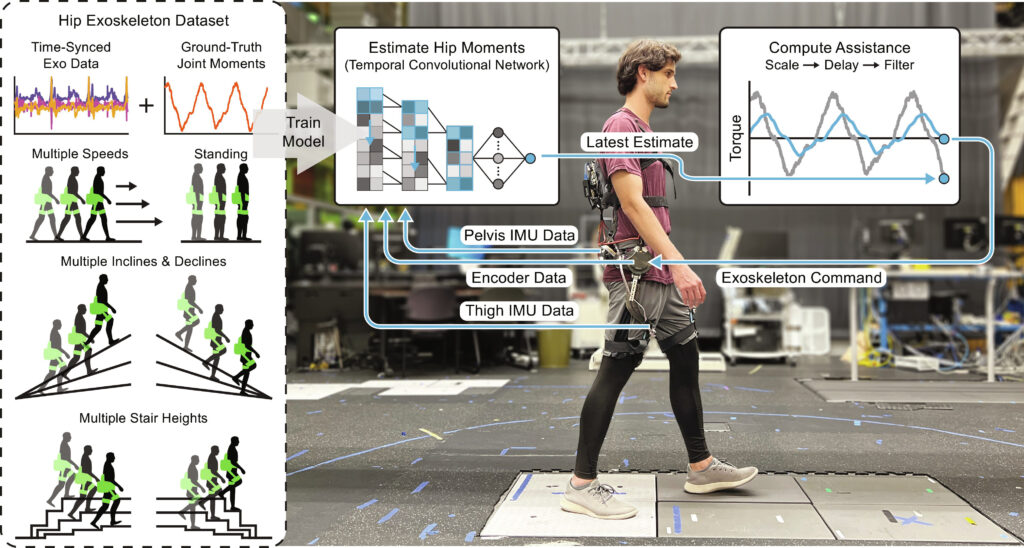
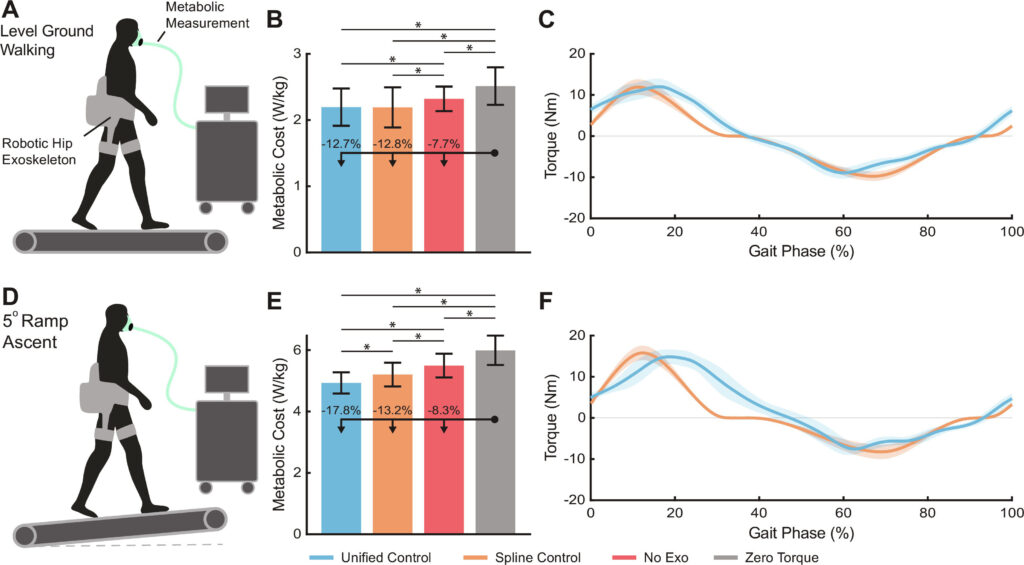
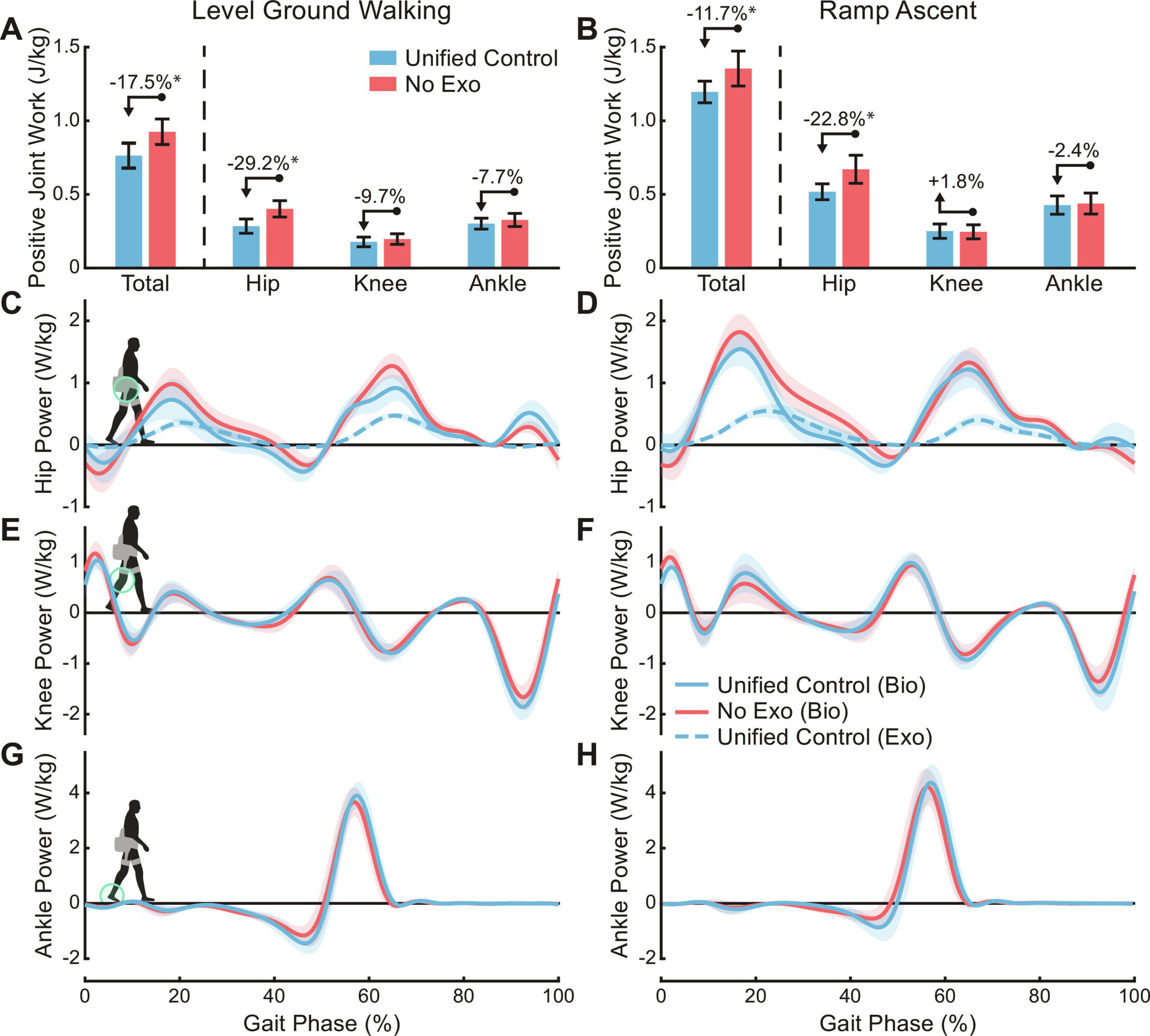
Estimating human joint moments unifies exoskeleton control, reducing user effort
Published in Science Robotics, this dataset consists of sensor data from a robotic hip exoskeleton and time-synced with ground-truth human lower-limb biomechanics. All data were sampled at 200 Hz.
- 34 subjects, 9 ambulation modes (e.g. level ground, ramp ascent/descent, stair ascent/decent, standing), 3 controllers (e.g. gait phase-based control based on biological torque, unified joint moment controller)
- Angles and Moments computed from Inverse Kinematics
- Processed sagittal plane hip, knee, and ankle angles
- Processed hip and knee extension moments
- Processed ankle plantarflexion moments
- Exoskeleton Sensor Data
- Actuators position and velocities from encoder
- Acceleration and gyroscope from IMUs
- Hip moment estimated by TCN
- Torque commanded to actuators
- Torque from the actuators (calculated by multiplying measured current by motor torque constant and gear ratio)
- Gait Phase
- Gait phase for each leg segmented by toe-off
- Gait phase for each leg segmented by heel strike
- Ground Reaction Forces
- Ground Reaction forces for each foot in 3 directions
- Center of Pressure for each foot in 3 directions